
Mobile users:
For best results, view in Landscape mode.
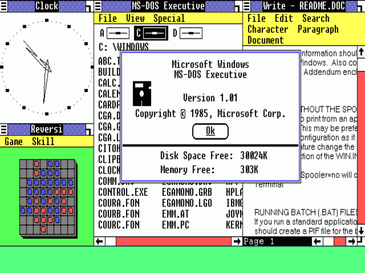
Windows 1.0:
Windows 1.0 was released on
November 20, 1985.
CGA/Hercules/EGA (or compatible)
MS-DOS 2.0
256 KB Ram
2 double-sided disk drives or a hard drive
The first version of Microsoft Windows included a
simple
graphics painting program called Windows Paint;
Windows Write, a simple word processor
an appointment calendar;
a card-filer; a notepad; a clock;
a control panel; a computer terminal;
Clipboard; and RAM driver.
Microsoft
Windows computing boxes, or windows represented
a fundamental aspect of the operating system.
Instead of typing MS-DOS commands windows 1.0
allowed
users to point and click to access the windows.
Windows 1.0 was Microsoft's attempt at a graphical
multitasking
operating system for the IBM PC.
Effectively a front end to MS-DOS, Windows 1.0 could run
multiple DOS based applications.
The
system requirements for Windows 1.0:
MS-DOS
2.0, 256 kB of RAM, an EGA
graphics adapter,
two floppy disk drives or a hard drive.
![]()
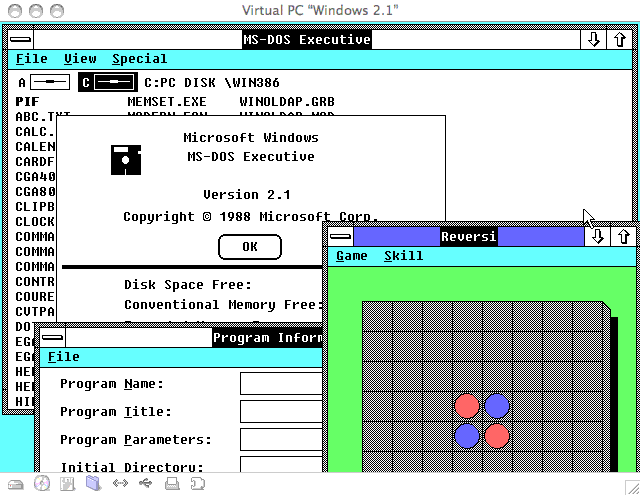
Windows
2.1:
Windows 2.1 was released on May 27, 1988.
Versions 2.0x used the real-mode memory model, whichconfined it to a maximum of 1 megabyte of memory.
In such a configuration, it could run under another multitasker
like DESQview, which used the 286 Processor.
MS-DOS version 3.0 or later 512 K RAM
One floppy-disk and one hard disk
Graphics adapter card
Microsoft mouse is optional
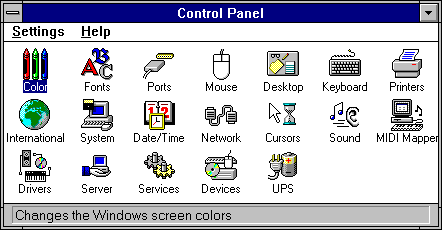
Windows 3.1:
In 1992 Microsoft released version 3.1 of its MS-DOS graphical
shell turned operating system.
Windows 3.1 became the first version of Windows to be widely
distributed with new PCs, cementing the dominance of Microsoft's
OS on the IBM PC platform and signaling the dawn of the
Golden Age of Windows.
System requirements for standard mode are:
* Intel 286 (or higher) processor
* 1 MB or more of memory (640K conventional and 256K extended)
* 6.5 MB of free disk space (9 MB is recommended)
System requirements for enhanced mode are:
* Intel 386 (or higher) processor
* 2 MB or more of memory (640K
conventional and 1024K extended)
* 8 MB of of free disk space (10.5 MB is recommended)

Windows 3.1 did not introduce much of anything new over
Windows 3.0.
Windows 3.1, however, was the first really
widely used version of Microsoft Windows.
Windows 1 and 2 were heavily
ignored or viewed as little
more than yet another DOS shell.
Even Microsoft's original
intention was to replace Windows
2.x with OS/2.
However, after IBM and Microsoft went their separate ways
Microsoft focused on delivering Windows 3.x while
building their own new "Windows NT" operating system,
with the intent of using Windows 3.x as a "stepping stone"
to get users to their NT based system.
This stepping stone lasted a
little longer than they wanted,
going through 95, 98 and finally ending with Windows ME.
There was also a less common
version of Windows 3.1 bundled
with Microsoft's MS-DOS based networking software
named "Windows 3.1 for Workgroups".
Regular Windows 3.1 did not
include any networking software,
but could run on top of any DOS based network such as
DEC Pathworks, or Microsoft Lan Manager.
An update, basically a service
pack, could
be applied to Windows 3.1 that brought
the version number up to "3.11".
"Windows 3.11 for Workgroups"
bundled an integrated
Windows 386-protected mode network system, replacing the
MS-DOS version.
![]()
Windows 95:

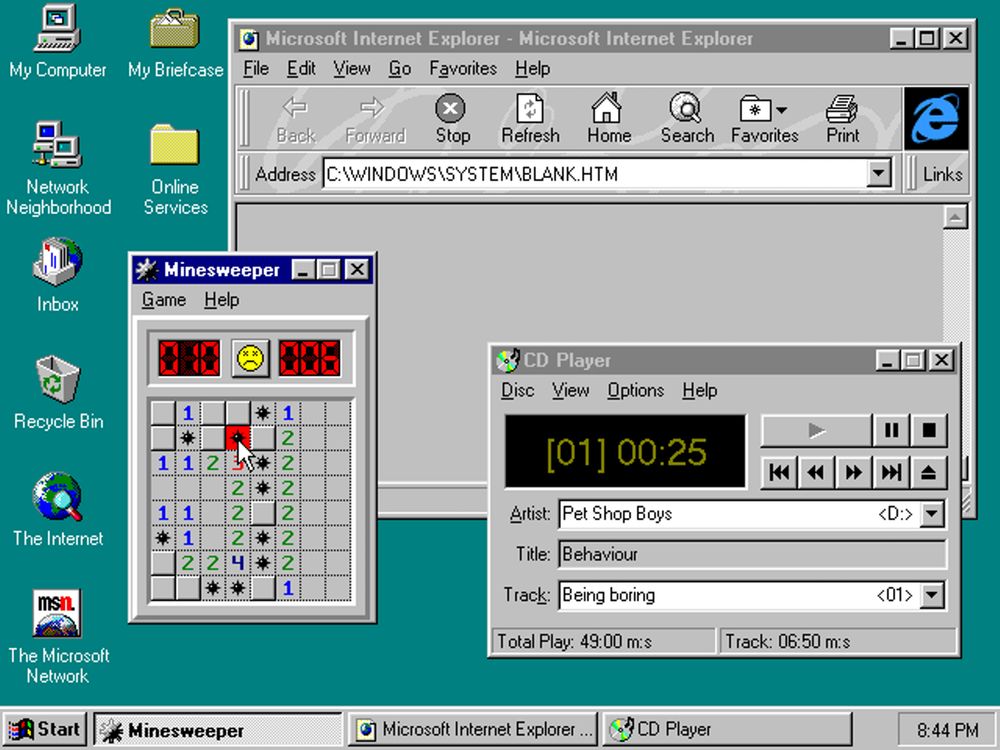
In 1995,
Windows 95 was launched.
The minimum hardware requirements for Microsoft Windows 95:
the MS-DOS operating system version 3.2 or later, or running
Microsoft Windows version 3.0 or later, or running OS/2
version 2.0 or later
4MB of memory (8MB recommended)
At least 70MB of available hard disk space for installation
Actual requirements may vary
based on
features you choose to install.
Therefore, on a 1GB drive, keep 100MB free.
VGA or higher resolution graphics card
Options, some of which are required by applications, include:
Mouse or compatible pointing deviceModem/fax modem
Audio card/speakers for sound
Windows 95 is a big successor
of Microsoft to their Windows
for Workgroups 3.xx.
It is no longer a graphic user interface on MS-DOS, but a
complete operation system.
Although users can see regular
MS-DOS window in the boot
process, the system take over MS-DOS 7.0 after it
loaded completely.
The windows control in Windows
95 was improved too.
The system box in the upper left of each window is designed
as an icon of the program.
In each window, the system box, "Minimize",
"Maximize/Restore"
and "Close" are usually located at the upper right corner.
In this version of Windows,
desktop was no longer a place to
display minimized icons.
Desktop now can not only store shortcuts and system icons
such
as new introduced "My Computer" and "Recycle Bin", but
also
store files and programs.
Before Windows 95, Microsoft
almost never provided functions that
could be accessed by a right click in Windows system,
from Windows 95, right click pop-up menu became more
popular and important.
User could use right click to
access the functions of "copy",
"paste" and "cut" almost everywhere in the system.
Some functions such as "properties" and quick "help" can
also be accessed conveniently.
Windows 95 came with an
improved help system, which added
another window to the left of the content window to show
index, and keywords.
The new help system can be displayed in any place of the
window
with any kind of size.
It also supported hyperlink with different functions, such
as
closing the help system.
Other features like Build-in network support with dial-up
for
TCP/IP protocol, support of 32-bit application, pre-emptive
multitasking and thread made Windows 95 stronger to meet the
requirement of Internet access and other complex tasks.
Windows XP:
On October 25, 2001, Microsoft released Windows XP.
The "XP" stands for eXPerience.
The OS lasted longer than any other version of Windows, from
2001 to 2007 when it was succeeded by Windows Vista.

System Requirements:
Processor: 300MHz or higher,
Memory: 128MB RAM or higher,
Hard drive disk free space: 1.5 GB or higher
(additional 1.8 GB for Service Pack 2
& additional 900MB for Service Pack 3)
The two primary versions of Windows XP:
Windows XP Home Edition and
Windows XP Professional.
The Home Edition was only 32-bit.
The Professional was 32-bit or 64-bit.
Windows XP included features that was not found in previous
versions of Microsoft Windows.
XP had a new interface -
A new look and ability to change the look.
Other features included:
Windows XP had faster start-up and hibernation sequences.
Fast user switching Enhanced device driver verification
(driver signing).
Code enhancements (better protection for code, less likely-hood
that somebody can come in and tamper with key system files).
Windows File Protection which, together with file signings,
discovers modified system files Encrypted File System (EFS)
which enabled you to encrypt files on our hard drive
IP Security (IPSec) enables us to encrypt data sent over
computer networks.
Clear type font rendering mechanism
(improved readability on LCD monitors).
Built in support for CD-RW.
Windows Messaging services Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
which enabled you to share one Internet connection with multiple
computers on a local area network (LAN).
Embedded firewall (Internet Connection Firewall – ICF)
Windows XP was designed to help bridge the gap between
Windows 9x/ME and Windows NT/2000.
The Windows XP upgrade was available for Windows 98, ME,
and 2000 users.
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a series of Microsoft
Windows computer operating systems produced from 1995 - 2000,
which were based on the Windows 95 kernel and its underlying
foundation of MS-DOS, both of which were updated in
subsequent versions.
This includes all versions of Windows 95
and Windows 98. Windows Me is sometimes included.
Windows XP uses the Windows NT 5.1 kernel, marking the
entrance of the Windows NT core to the consumer
market, to replace the aging Windows 9x branch.
The Windows NT (New Technology) kernel, or underlying code
upon which the interface (Explorer) runs, was completely new
and did not rely on DOS, despite the fact that it shared the same
shell (interface) as Windows 3.1.
Windows NT was originally designed to be used on high-end systems
and servers, however with the release of Windows 2000,
many consumer-oriented features from Windows 95 and
Windows 98 were included, such as the Windows Desktop Update,
Internet Explorer 5, USB support and Windows Media
Player.
The first versions of Windows (1.0 through to 3.11) were graphical
shells that ran from MS-DOS.
Later on, Windows 95, though still being based on MS-DOS, was its
own operating system, using a 16-bit DOS-based kernel and a
32-bit user space.
The kernel is a computer program that is the core of a computer's
operating system, with complete control over everything
in the system.
The kernel's vital function is that it enables the hardware and
software components to interact with each other.
On most systems, it is one of the first programs loaded on start-up
(after the bootloader).
It handles the rest of start-up as well as input/output requests from
software, translating them into data-processing instructions for the
central processing unit.
It handles memory and peripherals like keyboards, monitors, printers,
and speakers.
In 2014, when Microsoft officially ended support for the aging
operating system, Windows XP still accounted for 30% of
operating systems worldwide.
Computers running Windows XP will still work today, but they won't
receive any Microsoft Updates or be able to leverage
technical support.
Even though Microsoft will no longer release Windows XP security
patches you can still protect your computer.
But to secure your Windows XP system you should choose
a paid version of antivirus such as Norton Antivirus.
You can make Windows 10 look and sound like
Windows XP.
For the Windows XP Classic Start Menu,
Go to classicshell.net
or Download Here.
Also available is XP sounds:
Download Here.
Startup Sound Changer:
Download Here.
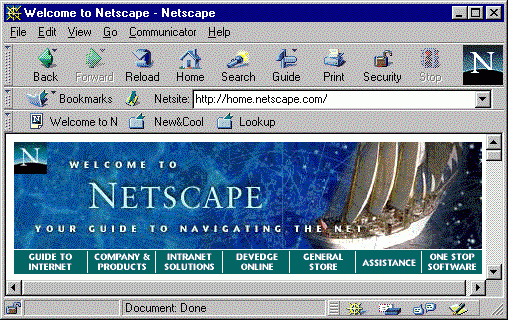
Netscape Navigator was the dominant web browser in the late
1990's, and Netscape Communicator was common
with many Windows XP users for designing websites, e-mail, and
newsgroups.
Netscape Communicator is a suite of Internet applications designed
by Netscape and released in 1997.
Netscape Communicator included:
Netscape Navigator (browser), Netscape Messenger
( newsgroups & pop Email ), and Netscape
Composer (html editor).
Netscape is no longer available.
However, if you want that Windows XP browser look and feel,
try SeaMonkey.
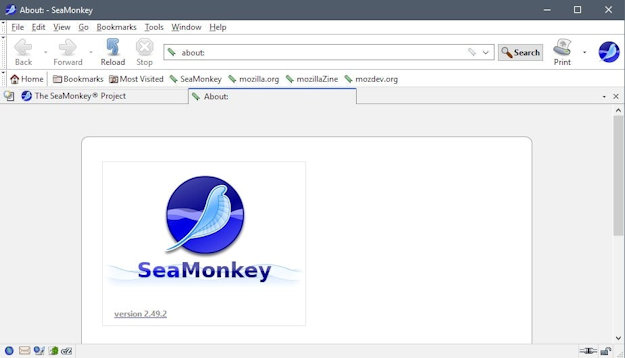
SeaMonkey has inherited the successful all-in-one concept
of the original Netscape Communicator, and it's compatible
with Windows 10.
PBL's Real Cars™ website was designed and maintained with
SeaMonkey's Composer.
For more information and even download SeaMonkey,
Go Here.
Floppy Disks:
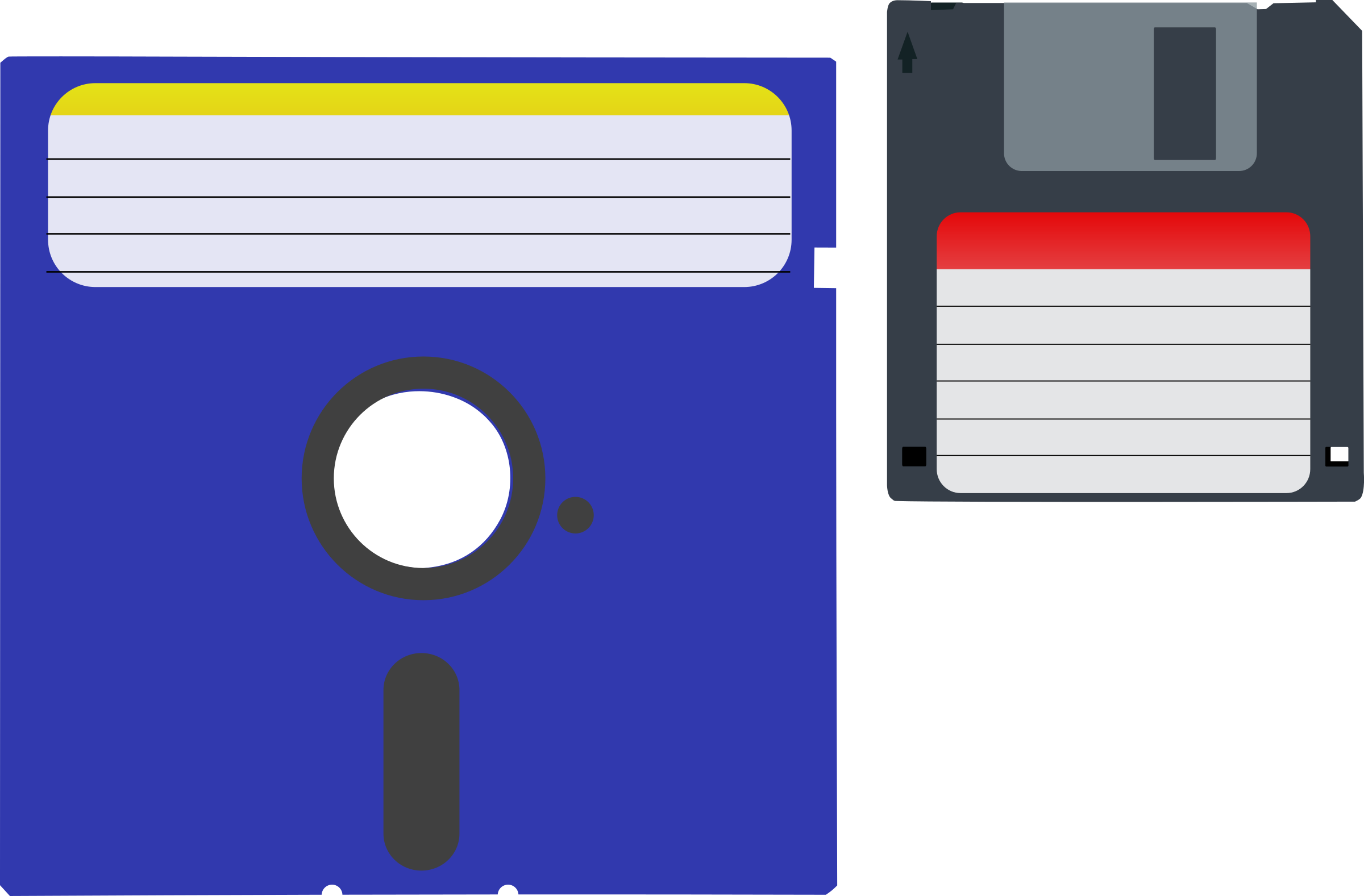
Floppy disks are read and written by a floppy disk drive (FDD).
The
diskette, or floppy disk was invented by IBM and in common
use from the mid 1970's to the late 1990's.
The first floppy disks were 8 inches, and later in came
5.25
and 3.5-inch formats.
The
first floppy disk, introduced in 1971, had a
capacity of 79.7 kB,
and was read-only.
A
floppy disk is called a floppy because the original
floppies
were 8 inches wide and the disk was made out of vinyl so
they
were really flimsy and "floppy" hence came the name
floppy.
The 5.25-inch diskettes were available in a
capacity of
160 KB single Side, 360 KB low-density and
1.2 MB high-density sizes.
By
1994, the 5.25-inch disk was extinct and was
replaced by
the preferred 3.5-inch disks.
The 5 1/4" floppy diskette was really floppy (flimsy),
hence the name.
The 3.5-inch floppy disk format was the last
mass-produced format,
replacing 5.25-inch floppies by the mid 1990's.
It was more durable than previous floppy formats since
the
packaging was rigid plastic with a sliding
metal shutter.
Online Services long before Facebook:

Click on logo for the old
Dial-Up looks & sound.
CompuServe
Prodigy online service
Juno online
service
GEnie
(General Electric Network for Information Exchange)
was an online service created by a General Electric
business.
A Usenet
newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet
system,
for messages posted from many users in different
locations using Internet.
Despite the name, newsgroups are discussion groups,
and are not devoted to publishing news, but were when the
internet was young.
Newsgroups
are still around today,
but only accessed with a fee.
![]() PBL's Real Cars Home
PBL's Real Cars Home
![]() PBL's Real
Cars Misc.
Stuff
PBL's Real
Cars Misc.
Stuff
![]() PBL's Real Cars Chapel
PBL's Real Cars Chapel
![]()